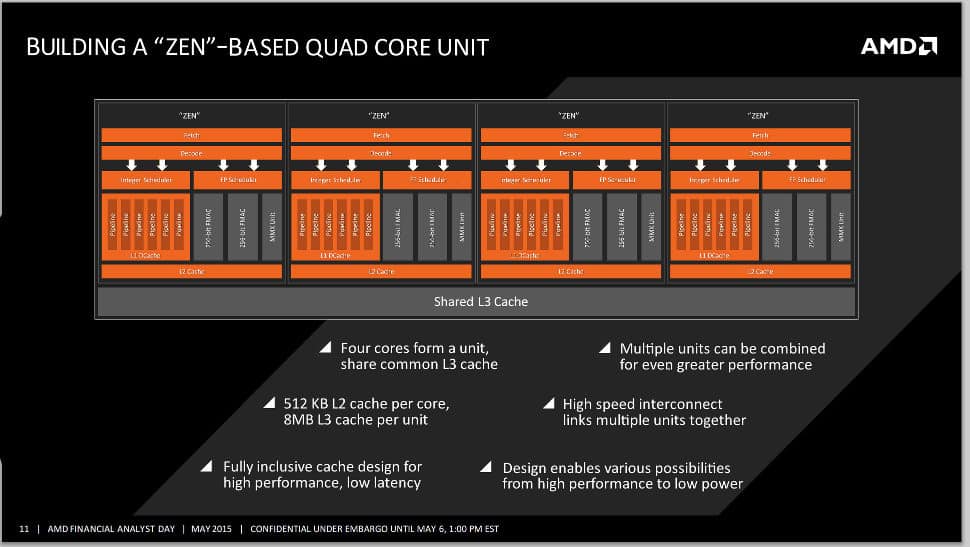
Another AMD slide has been leaked showing how their upcoming “Zen” cores will work together in a quad core unit. When the Zen CPU core block diagram was leaked we talked about how it is a monolithic core design and what sets it apart from its predecessor. Now with this leaked slide we can see that Zen cores share no hardware resources with each other except for a last-level cache (L3 cache), which is much like Intel’s current Haswell architecture.
This design is different from Haswell because Intel has shown it can put any number of cores on a chip and have them share a large L3 cache. We see this with Haswell-E with its 8 cores a 20MB cache, and Haswell-EX with 18 cores and 45MB of cache. Now with Zen the scaling up stops at 4 cores sharing 8MB of L3 cache. So you have a set of four cores making up what AMD is calling a “quad-core unit.” This is not a module, the cores will not share any hardware components with each other, besides the L3 cache.
So for AMD to build chips with more than four cores they will have to scale up the number of “quad core units”. A typical APU will more than likely feature just one unit with four cores and a high end desktop chip will have two units with 8 cores sharing 16MB of L3 cache, 8MB shared between the two quad-core units. The difference between the quad-core unit and a true module is that it is divisible, meaning in theory you can make dual-core parts using these units.
The way Intel does this with Haswell is that they disable two of the four cores on the chip. So a dual-core Haswell part has two cores disabled out of the physical four that are on the unit. Also the Haswell silicon has ring-stops that allow the designers to let the CPU access 2MB, 3MB, 4MB 6MB or all 8MB of the L3 cache.
It has not been revealed how AMD plans to package these chips. We could see AMD come up with a whole new high-end desktop processor package, one without integrated graphics on the silicon. This would have 8 cores, 16 MB of cache, dual channel DDR4 support, and a 40-lane PCI-Express root complex.
Source: TechPowerUp! | News Archive